

- #Ssh proxy for asycuda full
- #Ssh proxy for asycuda software
- #Ssh proxy for asycuda windows
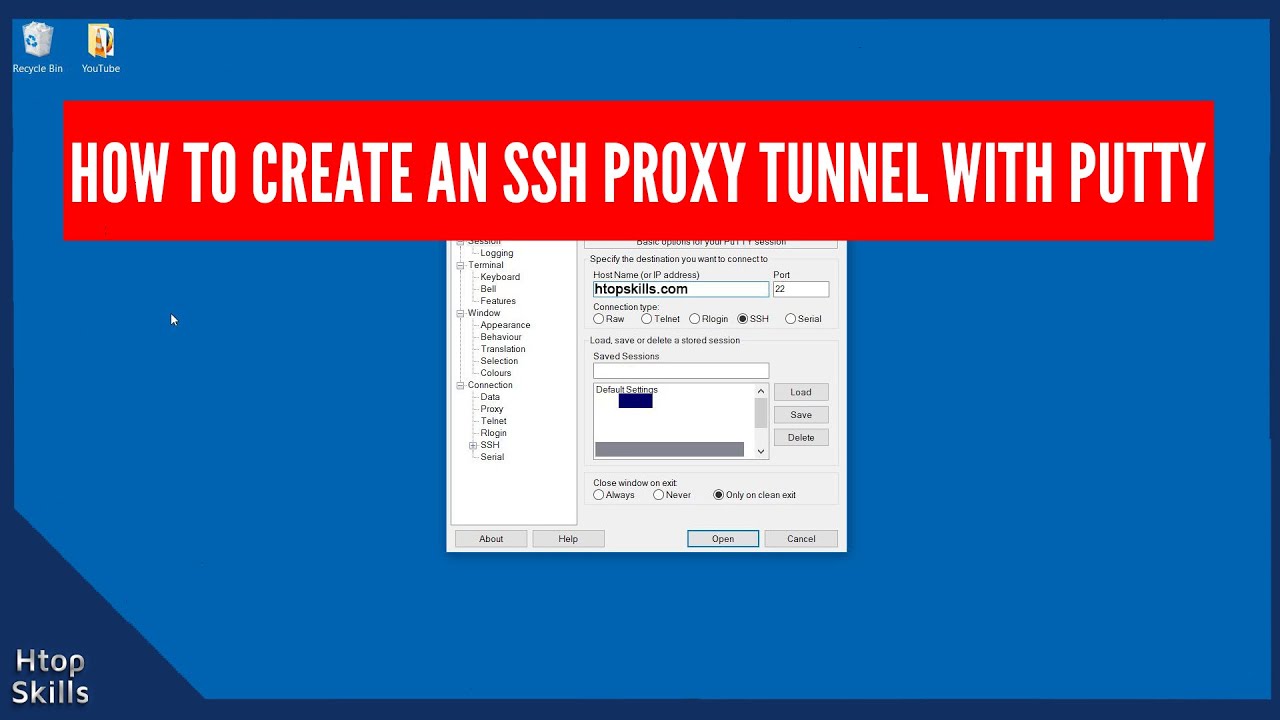
Once the tunnel is established, you now need to set up a SOCKS proxy in your web browser.ģ. This should open and terminal window and you should be prompted to login. You should see 'D31415' in the 'Forwarded ports:' box.Ħ. Under 'Destination' select the 'Dynamic' radio button and leave the 'Auto' button selected.ĥ. For 'Source Port' enter '31415' (this can be configured to whatever you want, just remember it).Ĥ. On the left side, in the Category window, go to Connection -> SSH -> Tunnels.ģ. Login to a linux machine and type "home" and this will display your homesite.Ģ.

The hostname should be your UCLA homesite followed by ".". Things you'll need: A Linux Mathnet account, PuTTY (ssh client), and Firefox.ġ.
#Ssh proxy for asycuda windows
This example shows a connection from a Windows machine using Firefox. A proxy setup can be configured using OSX, Linux, or Windows using various browsers. If you are browsing this site from off-campus, and you have a Mathnet Linux account, you can use this proxy setup to make it appear that your traffic comes from one of our IP addresses.
#Ssh proxy for asycuda full
In particular, connections to must come from a registered UCLA Math IP address to gain full access. It provides an alive checking mechanism.Some websites available to Math Department members are filtered by the network the traffic originates on. -M: Creates a direct tunnel on a port, loop-backed to a reverse one, echo_port.If we add authentication keys, as shown on our SSH keys tutorial, the tunnels will open without user intervention, as long as autossh is running. This utility can automatically create and recreate SSH sessions.
#Ssh proxy for asycuda software
Even if we can even configure the frequency and timeout for the session keepalives to facilitate the connection-loss detections, it would be nice to fully automate the SSH session creation and reconnection.įor that, a handy piece of software is autossh. Persistent Tunnelsīy the way, an SSH tunnel only exists as long as the SSH connection holds. Also, the host specification allows wildcards.
Reverse/callback tunnel on port 8022 in the loopback interfaces of the SSH server to our local client hostĪ lot of other options are available, like compression, Kerberos authentication forwarding, and many others. Direct tunneling from the local port 5432 to remote host 10.1.4.200 port 5432. This will connect to the remote SSH server on 10.1.4.100, using user ‘ baeldung‘, allowing: RemoteForward localhost:8022 localhost:22 In these files, we can specify default configurations to each commonly used endpoint, including forwarding tunnels and proxies: host 10.1.4.100 If it doesn’t exist, which is the default, we’ll have to create a new one. We can use the global ssh client config file (located on /etc/ssh/ssh_config or/etc/openssh/ssh_config) or use our user’s specific configuration file that is located at ~/.ssh/config. That’s why one of the most lovely features of ssh is allowing any command-line parameters in the config files. If disabled, other hosts on the SSH server network might use it. X11UseLocalhost: Forces the X11 forwarding to be only allowed from the SSH server host loopback address. X11Forwarding: Specifies whether X11 forwarding is allowed. PermitTunnel: Specifies whether tun device forwarding is allowed. PermitOpen: Specifies the address and ports a TCP forwarding may point to. It provides more fine control if we enable GatewayPorts. PermitListen: Specifies the addresses and ports that can be bound to allow port-forwarding to clients. By default, only the hosts running the SSH server can use reverse tunnels. GatewayPorts: Allows other hosts to use the ports forwarded to a client (reverse tunnels). Override, if enabled, all other related configurations options DisableForwarding: Disables all kinds of forwarding. It enables single TCP port forwards and socks proxying AllowTcpForwarding: Allows TCP port forwarding. AllowStreamLocalForwarding: Allows Unix domain sockets to be forwarded. Its location varies a little but is usually on /etc/ssh or /etc/openssh. The enablement of sshd, the daemon that serves ssh sessions, is done by editing the sshd_configfile.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
